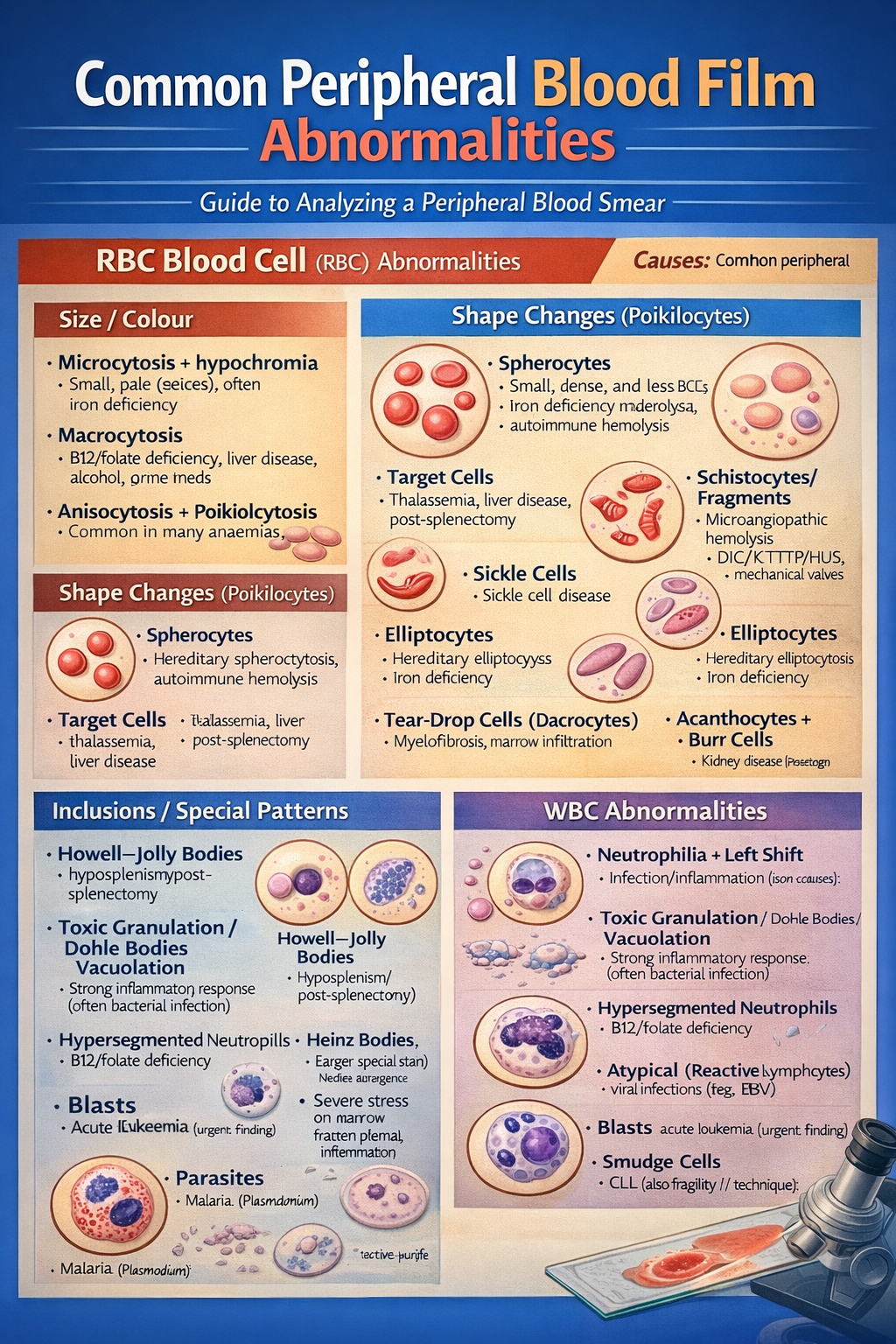
Common peripheral blood film (blood smear) abnormalities are usually grouped into red cells, white cells, and platelets:
Red blood cell (RBC) abnormalities
Size / colour
- Microcytosis + hypochromia (small, pale cells): often iron deficiency, thalassaemia
- Macrocytosis (large cells): B12/folate deficiency, liver disease, alcohol, some meds
- Anisocytosis (variable size) and poikilocytosis (variable shape): common in many anaemias
- Polychromasia / reticulocytosis (bluish larger young RBCs): blood loss or haemolysis, recovery after treatment
Shape changes (poikilocytes)
- Spherocytes (small, dense, no central pallor): hereditary spherocytosis, autoimmune haemolysis
- Target cells: thalassaemia, liver disease, post-splenectomy
- Schistocytes / fragments: microangiopathic haemolysis (e.g., DIC/TTP/HUS), mechanical valves
- Sickle cells: sickle cell disease
- Elliptocytes: hereditary elliptocytosis, sometimes iron deficiency
- Tear-drop cells (dacrocytes): myelofibrosis, marrow infiltration
- Acanthocytes (spur cells): severe liver disease, abetalipoproteinaemia
- Echinocytes (burr cells): kidney disease, sometimes artifact
- Rouleaux (stacked coins): high plasma proteins (e.g., myeloma, inflammation)
- Agglutination (clumping): cold agglutinin disease
Inclusions / special patterns
- Howell–Jolly bodies: hyposplenism/post-splenectomy
- Basophilic stippling: lead poisoning, thalassaemia, sideroblastic anaemia
- Pappenheimer bodies: sideroblastic anaemia, hyposplenism
- Heinz bodies (needs special stain): G6PD deficiency/oxidative damage
- Nucleated RBCs (NRBCs): severe stress on marrow, haemolysis, hypoxia, marrow infiltration
- Parasites: malaria (Plasmodium), sometimes others depending on region
White blood cell (WBC) abnormalities
- Neutrophilia with left shift (more bands): infection/inflammation
- Toxic granulation / Döhle bodies / vacuolation: strong inflammatory response (often bacterial infection)
- Hypersegmented neutrophils: B12/folate deficiency
- Atypical (reactive) lymphocytes: viral infections (e.g., EBV)
- Blasts: acute leukaemia (urgent finding)
- Smudge cells: classically CLL (can also be due to fragility/technique)
- Eosinophilia: allergy, parasites, some autoimmune/drug reactions
Platelet abnormalities
- Thrombocytopenia (low platelets): many causes; smear helps check for clumping
- Platelet clumping (pseudo-thrombocytopenia): EDTA-related artifact
- Giant platelets: increased platelet turnover or inherited platelet disorders
- Platelet satellitism (platelets stuck around neutrophils): artifact but can affect counts